More women are jailed in Texas, even though arrests have dropped. Why?
Cary Aspinwall, an investigative reporter for The Dallas Morning News, is a 2016 National Fellow.
Other stories in her series include:
Overlooked: As women go to jail in record numbers, who's watching out for their kids? No one.
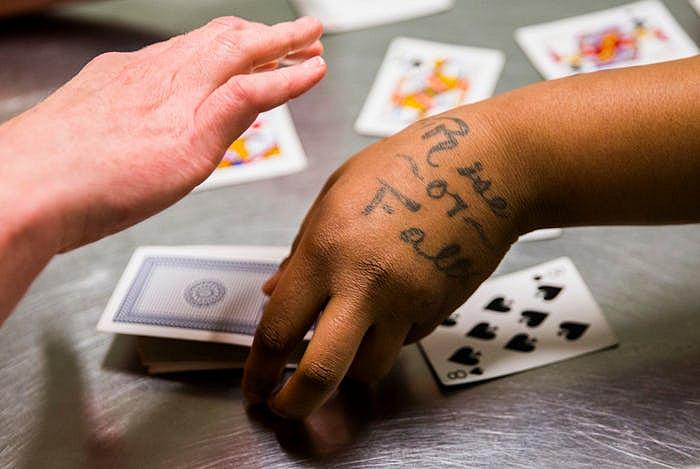

"Rise or Fall" is tattooed on the hand of inmate Sheniqua Miller as she and Stacy Jensen play cards in their unit at Burnet County Jail. Miller had probation but violated the terms, testing positive for marijuana. (Ashley Landis/Staff Photographer)
BURNET — Back when the county jail here housed maybe three women, jailers didn’t have to worry much about contraband mascara, tampon shortages or raunchy love notes in the intra-inmate mail.
But over the past decade, the number of female inmates in this rural jail northwest of Austin has surged. Instead of three women, the Burnet County Jail now houses as many as 140.
The situation here is an extreme example of a statewide trend. Across Texas, the number of women awaiting trial in county jails has jumped by 48 percent since 2011, according to an analysis of state data by The Dallas Morning News. At the peak this year in August, more than 6,300 women were jailed before trial, up from under 4,000 in early 2011.
Using monthly headcounts that sheriffs reported to the Texas Commission on Jail Standards, The News found significant increases in women inmates at many jails, especially in rural counties. After Burnet, the most substantial increases occurred in Harrison County on the Louisiana border and Brooks County in the state’s southern tip (see box below).
During the same time period, men in Texas county jails pretrial increased only 11 percent.
The surge doesn’t seem to reflect a crime wave. The number of women getting arrested has actually dropped by 20 percent since 2011, according to the Texas Department of Public Safety. (Arrest data doesn't necessarily reflect every time an inmate is jailed.)
And the number of women in state prison — where they usually serve time after sentencing — has been stable.
Source: Texas Commission on Jail Standards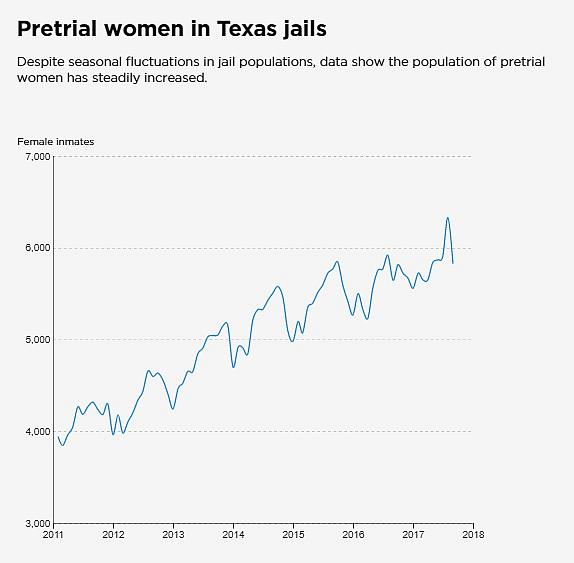
So what’s behind the increase in women in county lockups?
The News interviewed dozens of incarcerated women over the past year and examined the cases of many more. Though they were of all ages and races, most were poor. The majority were accused of crimes involving drugs or theft. Most had families to care for; few were flight risks.
We found two main reasons they were in jail awaiting what the state calls “final adjudication.” Some could not afford to post bondand get out on bail.
More commonly, they failed probation, which promises them clean records if they stay out of trouble. But they didn’t live up to the terms: They couldn’t pay their fees and costs, they failed drug tests, they didn’t turn up for court dates, they got arrested again.
They are women like Sheniqua Miller, 23, who had been on probation after selling fake drugs (really SweeTarts and Smarties candy) at the Whataburger in Burnet. Then came a misdemeanor theft charge and a drug test that showed marijuana use. So back to the county jail she went — for nearly two months.
“I just made bad choices, that’s all,” she said.
Though anecdotal, the cases examined by The News reflect some national trends identified by experts and advocates, who note that women in jail make up the fastest growing category of inmates in the country.
Women accounted for 14 percent of the jail population nationwide in 2014, up from 11 percent in 2000, according to a report last year from the federal Bureau of Justice Statistics.
About half the women behind bars in the United States are now held in jails, not state or federal prisons, according to a recent study by the Prison Policy Initiative, a justice-reform advocacy group. Only a third of male inmates are in jail.
Roughly 60 percent of women in jails nationwide have not been convicted of a crime, according to Aleks Kajstura, author of the study. Of that population, about 78 percent are accused of nonviolent crimes — mostly drug and property offenses.
Despite the steep increase in the number of women in county lockups, there have been few studies of them, Kajstura noted, wondering wryly how can we know so little about a population that gets counted at least once a day.
The big build
From the front, the Burnet County jail looks like an Elk’s Lodge or bingo hall, save for the razor-wire fence surrounding it. Texas Hill Country cloaks the bunker-like backside, designed to hold nearly 600 people.
The county began building the aspirationally large jail in 2007; it replaced an older lockup that had room for just under 100 inmates, including 12 women.
A local agency financed the new jail by selling almost $40 million in tax-exempt bonds, but a private contractor, LaSalle Corrections, initially ran the facility. In addition to county inmates, it housed prisoners for the U.S. Marshals Service and a drug treatment program for the Texas Department of Criminal Justice.
Inmate Beth Wesner, 25, sketches on her bunk at the Burnet County Jail in October. The jail had one of the most significant increases in female inmates in Texas, largely because it houses women for other counties that have run out of room. (Ashley Landis/Staff Photographer)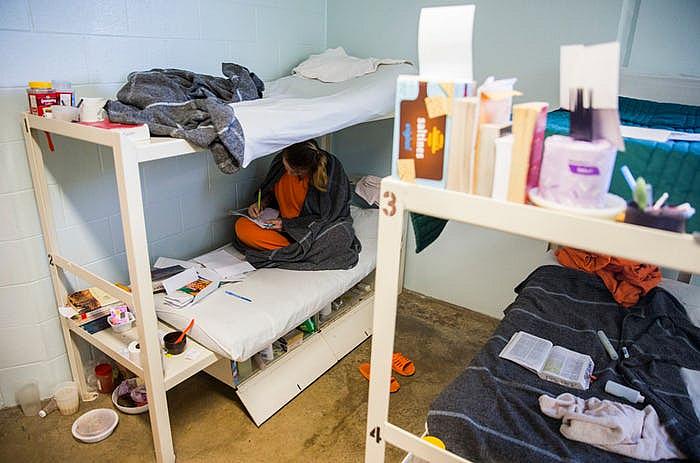
Local newspapers chronicled the struggle to keep the jail full. When a county judge told commissioners in 2011 about potential new contracts for housing state and federal inmates, the Burnet Bulletin quoted her saying: “This could be our Christmas present.”
The new jail had been pitched as a revenue generator that posed no risk to county taxpayers. But it didn’t work out that way: The state prison agency pulled out of its contract, and LaSalle did the same, saying it lost $4 million over five years.
County officials considered abandoning the massive, half-empty jail. Instead, Burnet spent $14 million to buy it from the finance agency that sold the bonds, and took over operations in April 2014.
So many county jails in Texas were scrambling for space to house female inmates that Burnet County inadvertently managed to capitalize on a trend. The population of women has shot up to 76 in a typical month.
On the October day The News visited the Burnet County jail, 60 percent of the 102 women there came from other counties in the area. Most were jailed on arrests involving drug possession and violations of the conditions of bail or probation.
At least one woman had been in jail for more than a week after being arrested in Lampasas County, 20 miles or so north of Burnet, on warrants for drug possession, letting her dog run loose and not paying court fines.
At least nine of the women had been in the jail for more than 100 days — awaiting trial.
Harder for women?
What would happen to your life if you went to jail for 30 days or more?
Would you lose your job? Custody of your kids? Your apartment or house?
Could you afford $5,000 in court fees or $500 a month in probation costs?
Missing a payment or failing to show up for a court date would increase your debt, and result in a new warrant for your arrest.
Then you’d likely go back to jail, facing a higher bond, or no bond, depending on the charges. You wouldn’t be able to renew your driver’s license or car registration until you paid your debt to the court.
Female inmates talk to visitors through glass in October at Burnet County Jail. The jail houses women from several other counties, whose family may travel two hours or more for weekly visits. (Ashley Landis/Staff Photographer)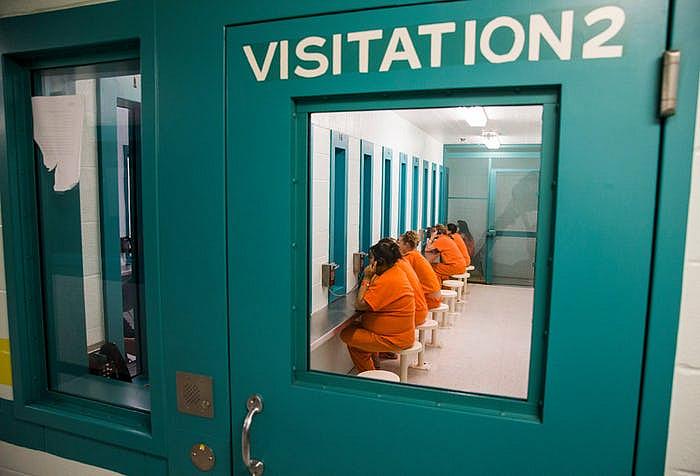
"The longer you hold somebody in jail, the more it hurts them, collaterally," said Nathan Hecht, chief justice of the Texas Supreme Court. "They lose jobs and have family problems and health issues — and it hurts taxpayers, 'cause they have to pay for all that."
Dealing with such a situation can be particularly difficult for women, experts say. They earn less than men (especially black and Hispanic women). One study found women who couldn’t make bailhad an annual median income of about $11,000.
When women are offered probation, the resulting fines and fees become an added economic burden. Many lack transportation, or don’t have anyone to watch their kids while they go to court.
“Texas has a miserable safety net for women and children,” said Rebecca Bernhardt, an advocate for criminal-justice reform. “If you’ve got no support and you get a criminal case, you’re toast.”
One report found that in 2014, women made up a quarter of all people on probation in the U.S. —but a significant portion of them end up in jail for technical violations, including failing to show up for check-ins or missing payments (in states like Texas, probationers must pay their own supervision fees). Other states, including Connecticut, have tried tailoring probation systems to account for women’s needs.
"There are so many things that women have to navigate, it's really hard if you have three kids," said Alison Brock, a policy analyst for the Texas Criminal Justice Coalition, a nonprofit, nonpartisan group dedicated to justice reform. She said the real issue isn't that more women are going to jail, it's that they keep going back — trapped in a cycle of debt and poverty and drug addiction.
Janet Ross, 47, recently spent three months in the Burnet County jail, 90 miles north of her home in Kerrville. A hairdresser, she lived most of her adult life without even a misdemeanor. But then, she said, she turned to meth after a bad divorce. For her first offense — she was picked up in June of 2014 for drug possession at a convenience store — she got probation.
But she violated it by getting arrested several times between 2015 and 2017, including four more arrests for drug possession, according to state records, in addition to bail jumping and failing to show up for a court hearing. Not long after we met her at the Burnet County jail, Ross was sent to a state prison drug treatment program.
In the arrest that landed her in jail, Ross said, she was walking with a male friend when the cops stopped them and found drugs on her. The guy didn’t go to jail, she said.
It’s not unusual that a boyfriend or husband is a reason women end up in the county jail, said Lt. Lou Armbruster. She’s a local who jokes about the jail being like a high school reunion. But because she runs booking and transport for inmates, she prefers they think of her as a stern disciplinarian.
“Often, their significant other is incarcerated somewhere as well, and that female is now trying to support her family via theft, forgery, credit card abuse or fraud,” Armbruster said.
Inmates Sheniqua Miller, 23, (left) and Stacy Jensen, 38, play cards in their unit at the Burnet County Jail. Both women are facing drug charges; Miller has been jailed there since October and Jensen has been in nearly six months. Jensen's bond is set at $300,000. (Ashley Landis/Staff Photographer)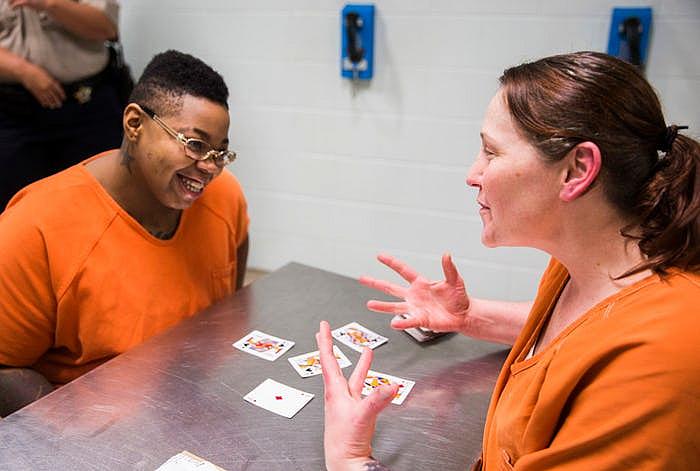
Many women need detox when they get booked in, she added. Often, they’re on a mix of prescription pills and meth, Armbruster said, but getting them to tell jail medical staff what they’ve taken is a challenge.
A combination of drug and theft charges has kept Stacy Jensen, 38, in the Burnet County Jail for nearly six months. We met her in October, telling other inmates’ fortunes with a deck of cards.
She was arrested on drug charges in Burnet County and a misdemeanor count of theft, after police found stolen Walmart items in a car she and her friends were in. Someone had called the police about a car allegedly full of “tweakers" under the influence of drugs.
At the time, Jensen was out on bail on charges of manufacturing or delivering heroin, which is why she’s still jailed, because her bond is now set at $300,000, records show. That’s higher than the bond for manslaughter in Dallas County, and nearly as high as the minimum bond for capital murder.
Jensen will probably remain in jail, 2 ½ hours away from her husband and children in Pleasanton, until a judge decides her fate.
Jacob Shivers, 8, with his mother, Melissa Ann Shivers, at their home in Northeast Philadelphia. Jacob tried to wake up his classmate Lucas Sims after he became "unresponsive" during story time at Loesche Elementary.
Drug addiction is the reason the jailers who work here end up guarding old friends and even their own family members, said Lt. Grayson Floyd, who oversees security and patrols the tidy, turquoise and yellow-striped hallways of the inmate housing units.
He said he’s learned a truth known by most who work in county jails: When a man gets locked up, the women in his life will sell the car, take a second mortgage on the house, pawn their jewelry, just to get him out on bail.
Nobody does that for women, he said.
For jailers, female inmates come with specific challenges: They use more toilet paper. Bras cost more than men’s underwear. The commissary has to stock tampons, and a sign by the jail’s front desk mentions strict rations for maxi pads. Makeup is forbidden, though inmates can buy cocoa butter lotion for $1.65 for 4 ounces.
And there’s another that has caused heartburn for Capt. Matt Kimbler, who runs the facility: Jailhouse love connections.
“It’s turning into Tinder,” Kimbler said. “It’s like, ‘swipe left, swipe right.’”
Kimbler jokes about the popular casual dating phone app, but the inmate love notes sometimes result in serious problems. A woman jailed in the medical unit with mental health problems has pledged herself as a “featherwood” girlfriend/slave to a male inmate in the jail affiliated with the Aryan Brotherhood of Texas.
Overall, the inmate-to-inmate mail had gotten too “Fifty Shades of Grey,” Kimbler said. He’s had to shut it down.
More jails may be dealing with these issues soon. While Texas closed eight prisons during the past six years, its counties have 15 local jails under construction and seven in planning stages, according to the state jail commission. Most are adding more space for women.
— Ariana Giorgi and Stephanie Lamm contributed to this story
[This story was originally published by Dallas News.]

