
KPCC’s Priska Neely reports on one of the reasons it has been so hard to bring down the black infant mortality rate: systemic racism is at the heart of the issue.

KPCC’s Priska Neely reports on one of the reasons it has been so hard to bring down the black infant mortality rate: systemic racism is at the heart of the issue.
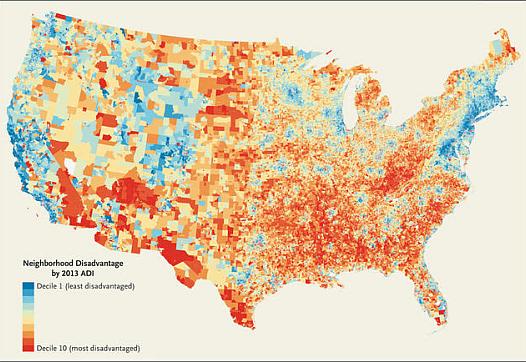
The Neighborhood Atlas gives journalists an intriguing new tool to visualize how social advantages vary across cities and regions.

This project received support from the Center for Health Journalism's California Fellowship and its Fund for Journalism on Child Well-being.
Other stories in the series include:
Black babies die at twice the rate of white babies. My family is part of this statistic
America's black babies are pay

The Castlemont neighborhood in East Oakland is known as a Best Babies Zone. The idea of this initiative is that improving life for everyone in the community will ultimately save babies.

In East St. Louis, the school district is helping parents get back on their feet.

It's one thing to identify the complex social cause of this crisis. It's far harder to combat racism and stop more babies from dying.

Local politicians have long tried to find ways to better serve residents of this poorer, unincorporated section of Sonoma. Two reporters are now asking whether annexation can improve health.

This project received support from the Center for Health Journalism's California Fellowship and its Fund for Journalism on Child Well-being....
This article was produced as a project for the Dennis A. Hunt Fund for Health Journalism, a program of the USC Annenberg Center for Health Journalism.